After deciding to study abroad, the next crucial step is figuring out how to choose universities. With advice from consultants, online resources, and peers often conflicting, making a choice can be challenging. This guide simplifies the process by focusing on essential factors like university rankings, job prospects, living costs, tuition fees, scholarships, and cut-off scores to help you make an informed decision 🙂
1. Choose your country for studying abroad
When choosing your universities, the first step is to determine which country best suits your needs. Consider the following factors:
Job opportunities
First, consider job opportunities. Each country has unique job markets that align with different fields.
For instance, if you’re studying computer science or data science, the USA, with its Silicon Valley, offers great prospects.
However, if you’re in mechanical or chemical engineering, Germany might be a better choice due to its strong automotive and chemical industries.
Therefore, before applying for higher studies in any country, explore the job opportunities available in your chosen field after graduation. This will help you determine which countries to shortlist based on the options available upon completing your degree.
If you dream to work at Google, have a look at Google’s headquarters at Silicon Valley:
Living expenses
Living expenses are a crucial factor when choosing a country for higher studies. Check student vlogs on YouTube and experiences shared on platforms like Quora to get insights into living costs. Many universities also provide estimates of living expenses.
Based on your budget for higher studies, you can identify which countries align with your financial situation. This will help you understand not only your expenses while studying but also what to expect once you start working in that country.
If you wish to know about the cost of studying in Singapore – tuition fees, living expenses, accommodation options, food, travel and miscellaneous expenses, you can check out the video below:
Tuition fees and scholarship availability
Choose your country based on your budget and financial options.
Studying in the US can be costly, with average master’s tuition ranging from 30-50 lakhs and limited scholarship availability. In contrast, many German and European universities offer numerous scholarships, allowing some students to study almost for free. Singapore also has a service obligation scheme that reduces tuition by 50% and typically has lower fees compared to the US.
Consider your budget and how crucial obtaining a scholarship is for you. Some scholarships only cover tuition, while others include flights and accommodation. Research the scholarship options listed on university websites before applying or making a decision.
To know about some scholarships that you must not miss, check out the video below!
2. Look at university rankings
Once you’ve shortlisted the countries, the next step is to examine university rankings.
Use Reliable Sources to check for university rankings. Some of them are: QS World University Rankings, Times Higher Education and US News Ranking (for the US).
Check for top universities: Focus on universities in the top 100 or 200 for better credibility.
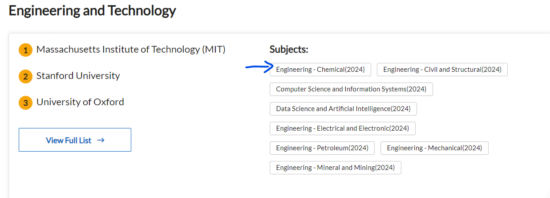
Consider Subject-Specific Rankings: Evaluate the strength of departments in your field of study. Example: UCB for Chemical Engineering is ranked #3, but its Arts department is #12.
Make your choice based on your interest and the ranking of that particular field globally.
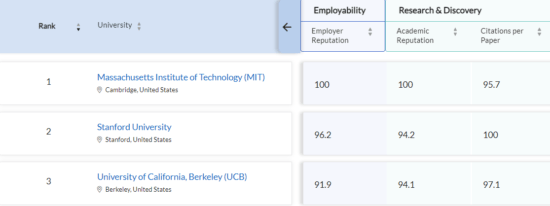
The step-by-step process to select is shown below with Chemical Engineering as an example.
3. Research to choose broadly 15-20 universities
After reviewing the university rankings, you’ll have a clearer idea of the top universities that offer the course you’re interested in. After this is done, follow the steps given below to arrive at the top 15-20 universities you could apply to.
Make broad shortlist: Review GRE, TOEFL, and CGPA cutoffs to estimate your eligibility and make a preliminary list of universities.
Example – for NUS Singapore’s M.Sc. in Biotechnology – the cutoffs are mentioned below.

LinkedIn Research: View LinkedIn profiles of alumni to see where they are studying. This helps you understand the universities that have accepted students from your college.
Take Initiative: Conduct this research yourself—no consultant or advisor can do this for you. Your personal effort will enhance the quality of your university selection.
Build and Refine Your List: Create a list of 15-20 potential universities and use this list to refine your choices further.

4. Narrow down further to find the best universities
Now that you have a broad shortlist of 15-20 universities, it’s time to narrow it down further. Follow the steps in this section to arrive at a final list of up to 10 universities you would like to apply to.
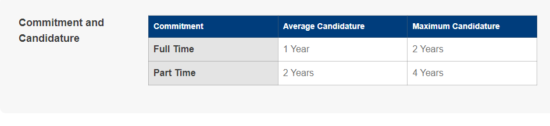
Examine Program Types: Understand the degree formats. Avoid short, professional master’s programs if they offer limited value. Opt for 1.5 to 2-year programs for a thorough education and more time to settle and seek internships. Example given for NUS MSc Biotechnology Program.
Review Course Content: Check if the courses align with your interests. For research programs, review research areas, faculty profiles, and their publications. An example for NUS, MSc in Biotechnology is shown below.
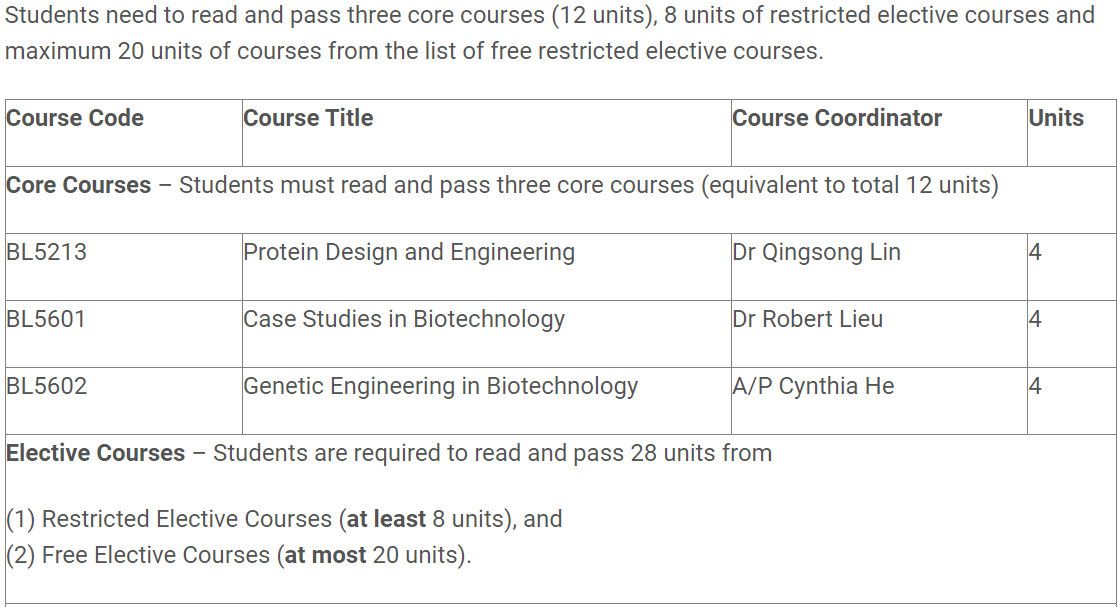
Evaluate Job Prospects: Research industrial partners and job opportunities linked with the university. Companies associated with the university are likely to offer internships and jobs.
Check Alumni Success: Use LinkedIn to see where alumni work. This helps gauge potential job prospects and employer preferences.
Further Refine Your List: Narrow down to 6-10 universities that best fit your goals and interests.
5. Categorise universities as safe, moderate and ambitious
Once you have your final shortlist of 10 universities, ensure they fall into three categories: safe, moderate, and ambitious. The categorisation is explained in detail below:
Safe Universities: Choose ones where you’re confident of acceptance but ensure you’d still be willing to study there if they were your only option.
Moderate Universities: Select schools where your profile matches the average admitted student, providing a balanced chance of acceptance.
Ambitious Universities: You should choose ambitious universities which are really good universities but your chances to get in might be slim e.g. it could be Georgia Tech or Columbia or Cornell university.
Final List: Aim for a mix of 3 safe, 3 moderate, and 3 ambitious universities to create a well-rounded list.
This approach increases your chances of receiving offers from at least 50% of the universities you apply to, providing you with a backup while also allowing you to challenge yourself by applying to more competitive options. This balance will help you feel both secure and ambitious in your application process.
To know more about shortlisting universities using AI tools check out the video below:
With these steps, you’re well-equipped to make an informed decision about your study abroad journey. All the best!!
To help you in your study abroad journey – you can sign up for our course – Write your Way to Study Abroad.
For all any queries, feel free to leave a comment and we will get back to you as soon as possible!




