Imagine submitting an important assignment or research paper, only to realize later that you’ve unintentionally plagiarized. It’s a common mistake that can have serious consequences. In this blog, we’ll break down what is plagiarism and how to avoid it through proper quoting, paraphrasing, and summarizing, and highlight useful tools for detection. Whether you’re a student or researcher, mastering these skills will ensure your work maintains academic integrity.
What is Plagiarism?
Plagiarism is the unethical practice of using someone else’s ideas, words, or expressions without proper acknowledgement. It can occur intentionally, such as when a writer deliberately presents another person’s work as their own, or unintentionally, when individuals are unaware of what constitutes plagiarism.
This includes not just direct copying of text but also the appropriation of ideas, images, or data without crediting the original source. Plagiarism is considered a serious offence in academic and professional settings, as it undermines the integrity of research and scholarship.
Have a look at the schematic below to understand how big a role plagiarism checking plays when you want to publish an article.
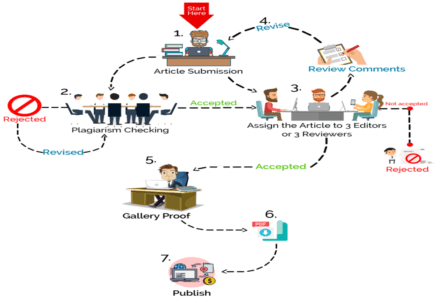
Types of Plagiarism
Direct Plagiarism: This occurs when someone copies another author’s work word for word without citation. This type is the most straightforward form of plagiarism and is easily identifiable.

Self-Plagiarism: This refers to reusing your previously published work without acknowledgement. Even if the author is the same, it’s important to cite earlier works to maintain transparency and integrity. Shown below is a way on how you can do this:

Mosaic Plagiarism: This happens when a writer intersperses their own words with phrases from a source without proper citation, even if the wording is altered slightly.
Accidental Plagiarism: Often a result of negligence, this form occurs when individuals fail to cite sources correctly or misquote them, leading to unintentional plagiarism.
How to Avoid Plagiarism
Quoting: When you want to include someone else’s exact words in your writing, use quotation marks around the text and provide an appropriate citation. This method clearly indicates to your readers that these words are not your own, maintaining the integrity of your work. Look at the example below on how to do this:

Paraphrasing: This involves rewriting the original text in your own words while still conveying the same idea. It’s essential to change both the wording and the structure of the original sentences, not just swap out words for synonyms. Proper citation is still required to credit the original source. An exmaple is shown below:

Summarising: This method condenses the main ideas from a source into a shorter form. When summarising, you must still use your own words and provide a citation. Summarising is useful for integrating information from multiple sources while providing a concise overview. An example screenshot from a review paper is shown below:

To learn how you can use AI tools to do this, check out the video below:
Plagiarism Detection Tools
There are several tools available to help identify and correct potential plagiarism in your work. Here are some popular options:
1. Turnitin:
This widely used tool checks your papers against an extensive database of student work, publications, and online sources. Once you submit your assignment, Turnitin generates an originality report showing the percentage of your text that matches other content. This percentage represents a similarity index, not a direct measure of plagiarism. A sample report is shown below:

What should you do with this report? Use your judgement to evaluate the highlighted text. If you’ve quoted directly and cited the source, it may be flagged as similar, but you haven’t committed plagiarism. In contrast, if you’ve paraphrased poorly—changing only a few words—Turnitin will also flag this as similar. In this case, rephrase the sentences more thoroughly to ensure they are in your own words. While Turnitin is a valuable tool, it’s essential to understand what constitutes plagiarism and what does not.
2. Grammarly:
While primarily a writing assistant, Grammarly also includes a plagiarism detection feature. It checks your text against billions of web pages to find any matching content and provides suggestions for improving originality.

3. Plag.ai:
This is an AI-driven tool that allows you to check up to 4,000 words for free. For a small fee, you can access more extensive checks. It’s user-friendly and effective for detecting similarities in your writing.
4. Quetext:
Another useful tool, Quetext offers a free plagiarism detection service with a deep search capability. It’s particularly helpful for students and researchers looking to ensure their work is original.

5. Paperpal:
Paperpal is a plagiarism detection tool that scans documents for originality, providing a similarity report and citation suggestions to maintain academic integrity. Note that Paperpal uses Turnitin integration.
To know more about this new tool, check out the video below:
Avoiding plagiarism is not just about avoiding trouble; it’s about respecting intellectual property and contributing ethically to academic and professional communities. By using the right methods—quoting, paraphrasing, and summarising—and utilising detection tools, you can ensure your work is original and credible.
For more detailed learning on writing and publishing research papers, you can check out our course – A-Z of Research Paper Writing and Presentation
Happy writing, and best of luck with your academic and research endeavours! For any queries, comment below and we will try to get back to you as soon as possible.




